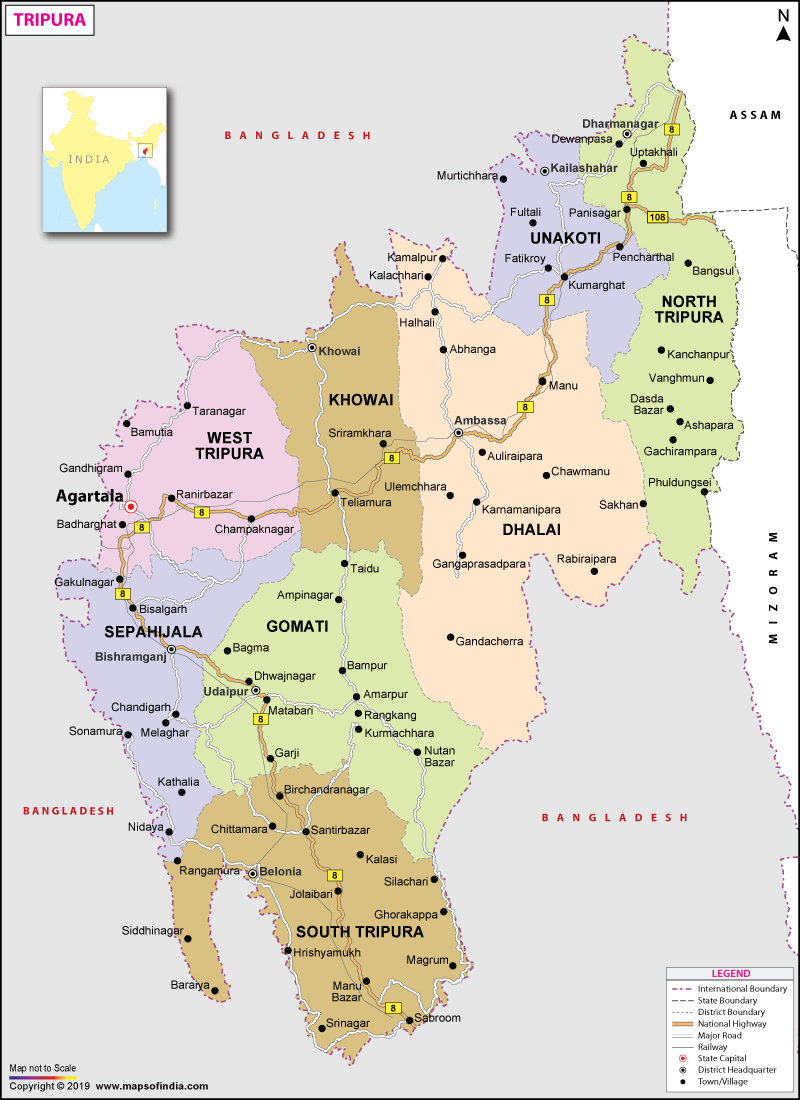
| *Map of Tripura with major roads, railways, rivers, national highways, etc. |
| Disclaimer: All efforts have been made to make this image accurate. However Mapping Digiworld Pvt Ltd and its directors do not own any responsibility for the correctness or authenticity of the same. |
Tripura is one of the Northeastern seven sister states in India. In fact, it is the 3rd smallest state of India and covers an area of 10,486 square km.
The state is surrounded by Bangladesh on its north, west and south. On its eastern side, it is surrounded by the state of Mizoram and Assam. Agartala is the capital of this state. As per the 2011 census, the population of the state is 36,73,032. It constitutes around 0.3% of the total population of the country. The indigenous communities that are known as ST (Scheduled Tribes) in India form 30% of the population in Tripura. The state has 19 tribes, and it is an eco-friendly and pollution-free state.
The languages that are mainly spoken in this state are Kokborok and Bangla. This state was ruled by the Tripuri dynasty for many centuries. It was considered as a princely state at the time of the British rule. In the year 1949, it became a part of independent India. The ethnic strife and conflict between the Bengali population and indigenous people have led to scattered violence and tension since the integration of this state in India. On the other hand, the institution of an independent tribal administrative organisation and various strategies have calmed the situation. National Highway 44 is the only main highway that connects this state with the rest of India.
| Facts on Tripura | |
|---|---|
| Official Website | www.tripura.nic.in |
| Date of Formation | Jan 21, 1972 |
| Area | 10,491.69 km2(4,050.86 sq mi) |
| Density | 350/Km2 |
| Total Population (2011) | 3,671,032 |
| Males Population (2011) | 1874376 |
| Females Population (2011) | 1799541 |
| No. of District | 8 |
| Capital | Agartala |
| Rivers | Burima, Gomati, Khowai, Dhalai, Muhuri, Feni, Juri etc. |
| Forests & National Park | Clouded Leopard NP, Rowa WS, Bison's NP, Trishna WS |
| Languages | Bengali, Kokborok, English, Noyakhali, Chakma |
| Neighbour State | Assam, Mizoram |
| State Animal | Phayre's Langur |
| State Bird | Green Imperial Pigeon |
| State Tree | Agar |
| State Flower | Nageshwar |
| Net State Domestic Product (2011) | 50750 |
| Literacy Rate (2011) | 87.75 % |
| Females per 1000 males | 961 |
| Assembly constituency | 60 |
| Parliamentary constituency | 2 |
In Sanskrit, Tripura means 'three cities'. Paleolithic tools that are made from fossil wood are found in Khowai and Haora valleys. The state is mentioned in all the Indian epics like the Mahabharata, the Puranas, and the Edicts of Ashoka. Kirat Desh is the old name of Tripura. But, it is not clear whether Kirat Desh is coterminous with modern Tripura. The entire region of this state was ruled by Twipra kingdom for many centuries. As years passed by, the boundaries of the kingdom have changed. The state is house to various royal palaces as well as temples that attract tourists and vacationers from across the world. Agartala, the capital city, is a popular sight-seeing location.
Tripura became the princely state at the time of British rule in India. Udaipur that was located in the southern part of this state was the capital of Twipra Kingdom. Bir Chandra Manikya modelled and displayed the administration on the British India pattern. He also enacted reforms that include the formation of the Municipal Corporation of Agartala. After India gained independence in the year 1947, the Tippera district became a part of East Pakistan. The Tripura Merger Agreement was signed by the Maharani Regent in the year 1949. In the year 1956, the state became a union territory. An elected ministry was set up in the year 1963.
Tripura is one of the smallest states of India after Sikkim and Goa. You can use the national highway in order to reach this place. The highway passes through the Mamit and Karimganj district of Mizoram and Assam respectively. The physiography of the state is characterised by plains, valleys and hill ranges. Tripura has five anticlinal hill ranges that run from north to south. They also run through Shakhan, Longtharai, Japui Hills and Athamura in the eastern side and Boromura in the western side. The intervening and prevailing synclines are Agartala-Udaipur, Kamalpur-Ambasa, Khowai-Teliamura, Dharmanagar-Kanchanpur and Kailasahar-Many valleys. The highest point of the state is Betling Shib that is located in Jampui range. The altitude of Betling Shib is 3,081 feet or 939 meters.
The isolated hillocks that are scattered throughout this state are called tillas. On the other hand, the narrow alluvial valleys that are located on the western side are known as lungas. There are various rivers that originate from the hillocks and flow in Bangladesh. The Dhalai, Khowai, Juri, Longai and Manu flow to the northern side, Feni and Muhuri in the southwest side and the Gumti in the western side. The winter season is from December to February, monsoon season from May to September, summer or pre-monsoon season from March to April, post-monsoon season from October to November. At the time of the monsoon season, the state witnesses frequent floods due to heavy rains.
In terms of the population in the Northeastern part of India, Tripura holds the second spot after Assam. As per the census that was conducted in the year 2011, the total population of the state is 3,671,032 . The state constitutes 0.3% of the total population of India. The male to female ratio of this state is 1000:961 which is higher as compared to the national sex ratio of 1000:940. The population density of the state is 350 persons/square km. In the year 2011, the rate of literacy was 87.75% that is higher as compared to the national literacy rate of 74.04%. Bengalis represent a major portion of the population of the state. The state has nineteen ethnic groups, as well as sub-groups with different cultures and languages. The largest group in the state was Tripuris who speak Kokborok. The other groups that are present in this state, along with their population are Reang, Chakma, Jamatia, Mog, Halam, Kuki, Munda and Garo. The language that is mostly spoken is Bengali due to a high percentage of the Bengali population in this state. Kokborok is the language that is prominent among the tribal population.
The state of Tripura is ruled by a democratic parliamentary system. The residents of this state are granted universal suffrage. The government of Tripura has three branches: judiciary, legislative and executive. The Legislative Assembly of Tripura consists of office bearers and elected members that are chosen by various members. The Speaker controls the assembly meetings and conferences. In the absence of the Speaker, a Deputy Speaker conducts the meetings. The members of the Legislative Assembly are elected for a period of five years. The judiciary or magistrate is selected by the High Court of Tripura. In addition, the Indian President appoints the Governor of this state and the Governor appoints the Chief Minister. The governor appoints the committee of ministers after getting the advice and recommendations of the Chief Minister.
Tripura sends one and two representatives to Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha respectively. The local body elects panchayats for different villages in this state. The two political parties of this state are INC (Indian National Congress) and the Left Front.
The schools in this state are controlled by private organisations and the state government that includes religious institutions. The medium of instruction in most of the schools is Bengali or English. On the other hand, various regional languages are also used like Kokborok. The schools in this state are mainly affiliated to CBSE, NIOS, TBSE and CISCE. The schools use new educational techniques and tools to provide modern education. There is a private university and a central university in the state. In addition, there are general colleges and also colleges for engineering, medical, law, art and music. There are also a few polytechnic colleges.
Tripura Board 12 Class ScheduleThe primary sector of the state consists of mining, forestry and agriculture. Secondary sector that includes manufacturing and industrial sector contributes a higher percentage to the GDP of this state. Maximum workers in the state are involved in the retail sector after agriculture. It is followed by the manufacturing sector, public administration and education. In this state, a lot of people are dependent on allied activities and agriculture. Rice is the main crop of Tripura. The other crops that are cultivated in this state are jute, pulses, Mesta, sugarcane and potato. The main horticultural products are pineapple and jackfruit.
The diverse groups of this state have led to a multiple and composite culture. The various ethnic groups of the state are Bengali, Tripuri, Manipuri, Reang, Jamatia, Koloi, Noatia, Chakma, Murasing, Garo, Halam, Mizo, Kuki, Munda, Mogh, Santhal, Uchoi and Oraon. The Bengali population constitutes the largest community of this state. Due to this reason, Bengali culture is considered as the main non-indigenous culture. A lot of tribal families that live in the towns have embraced the Bengali language and culture. Tripuri kings are considered as the greatest patrons and supporters of Bengali culture, particularly literature. Bangla was also the court language. Bengali cuisine, music and literature are widespread, mainly in urban areas. Tripura is famous for cane handicrafts and bamboo, and these are mainly utilised for making a wide range of utensils, furniture, fans, mats, replicas, baskets, materials for interior decoration and idols. Dance and music are an integral part of the culture in this state. Local instruments like sumui (a kind of flute), chongpreng and sarinda (string instruments) are quite popular in this state. The indigenous communities have their own collection of dances and songs that are performed at the time of religious occasions, weddings and other events. The 'Goria dance' is performed by Jamatia and Tripuri people at the time of Goria Puja. Some of the dance forms of Tripura are jhum dance, mamita dance, lebang dance, mosak sulmani dance etc.
The main languages that are widely spoken in this Northeastern state are Kokborok and Bengali. In addition, various minority languages are also spoken in this state. English is also used for official purpose. The widely spoken language is Bengali as the state has a large number of Bengali population. On the other hand, the language of Kokborok is quite prominent among the tribal population. Sabrum and Chakra are the main Bengali languages that are spoken by the tribal population. A number of individuals also speak Rankhal and Halam. It is a language that originates from the Halam language.
If you want to visit this state, then you can explore the various mesmerizing places that are located here. The state has many natural charms. The sightseeing tour of this state will provide a delightful and charming experience for a tourist. There are various architectural wonders in this state like Kunjaban and Neermahal Palace. It is considered as the ideal tourist spot in the Northeast part of India. Kamalasagar Kali and Bhuvaneswari temple are the two holy places in the state. Many pilgrims and tourists visit Tripura in order to see the famous temples of this region. There are various wildlife attractions in Tripura. The wildlife lovers will certainly want to come to this state for visiting the various wildlife destinations. Gumti Wildlife Sanctuary is home to elephants, barking deer and bison. Sepahijala Sanctuary offers shelter to the migratory birds. Trishna and Rowa Wildlife sanctuary are also famous and renowned for wildlife species. The attraction spots of Tripura also cover a number of astounding royal places, such as Neermahal Palace. It is a famous palace that was built by incorporating the styles of Muslim and Hindu. Ujjayanta Palace is another well-known tourist spot in Agartala, Tripura. Kunjaban Palace is also a famous destination for sightseeing.
National Highway (NH) 44 is the only main road that connects this state to the rest of the country. It starts at Sabroom located in the Southern part of Tripura. It then heads to the northern side of Agartala, the capital city of Tripura. After that, it turns to east, northeast and enters Assam. The highway is also called the 'Assam Road', and it is considered as the lifeline of the state. Manu is a town in the district of south Tripura that is connected by another highway NH 44A with Aizawl, the capital city of Mizoram.
Agartala is well-connected by air. The airport is located in the capital city, Agartala that connects it with other Indian cities. In addition, there are also connecting flights to Mumbai, Ahmedabad, Chennai, Bangalore, Guwahati, Aizawl, Silchar, Delhi, Imphal and Kolkata. The airport in Agartala is the second busiest airport after Guwahati airport in the Northeast. Tripura has the international border of 856 km with Bangladesh. The main railway station in Tripura that connects to the railheads of Kolkata, Delhi, Indore, Chennai and Bangalore is in Kumarghat. There is also a bus service between Dhaka, the capital city of Bangladesh, and Agartala.
MOI.AB.02.02.17