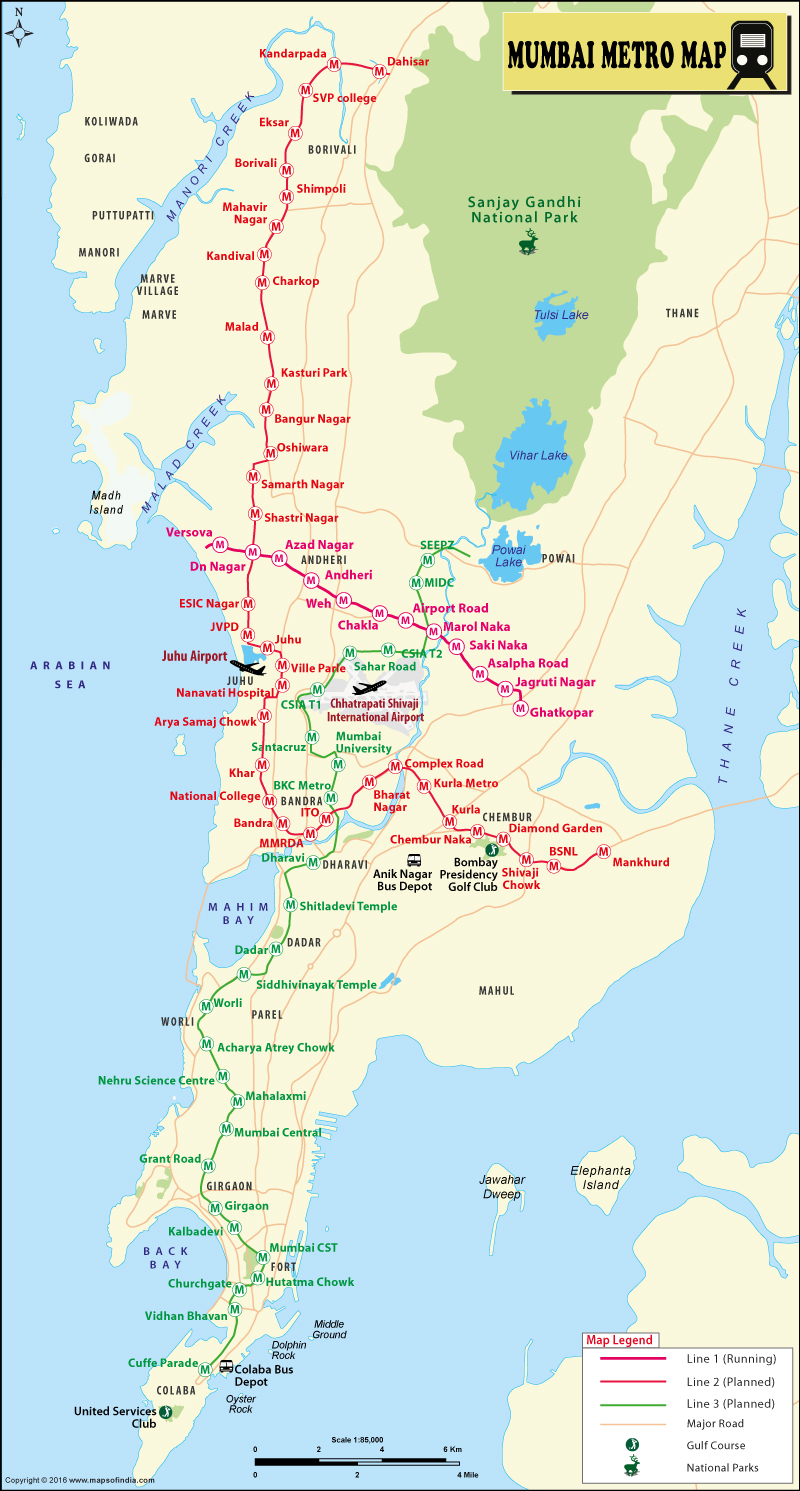
| Map shows the Metro Rail Network in Mumbai City. |
| Disclaimer: All efforts have been made to make this image accurate. However Mapping Digiworld Pvt Ltd and its directors do not own any responsibility for the correctness or authenticity of the same. |
The frequency of Mumbai Metro Trains on Weekdays (Monday to Saturday) will be 4 minutes at peak hours while in non-peak hours it is 8 minutes. On Sunday or Public holiday the frequency of each metro is 8 minutes.
| 1 | Versova |
| 2 | D N Nagar |
| 3 | Azad Nagar |
| 4 | Andheri |
| 5 | Western Highway |
| 6 | Chakala JB Nagar |
| 7 | Airport Road |
| 8 | Marol Naka |
| 9 | Saki Naka |
| 10 | Asalpha |
| 11 | Jagruti Nagar |
| 12 | Ghatkopar |
| 1 | Charkop |
| 2 | Malad |
| 3 | Kasturi Park |
| 4 | Bangur Nagar |
| 5 | Oshiwara |
| 6 | Samartha Nagar |
| 7 | Shastri Nagar |
| 8 | D N Nagar (Line 1 Interchange) |
| 9 | ESIC Nagar |
| 10 | JVPD |
| 11 | Juhu |
| 12 | Vile Parle |
| 13 | Nanavati Hospital |
| 14 | Aryasamaj Chowk |
| 15 | Khar |
| 16 | Barat Nagar |
| 17 | National College |
| 18 | Bandra |
| 19 | MMRDA |
| 20 | Income Tax Office |
| 21 | Complex Road |
| 22 | Kurla |
| 23 | Barve Marg |
| 24 | RC Marg |
| 25 | Shivaji Chowk |
| 26 | BSNL |
| 27 | Mankhurd |
| 1 | Cuffe Parade |
| 2 | Vidhan Bhavan |
| 3 | Churchgate Metro |
| 4 | Hutatma Chowk |
| 5 | CST Metro |
| 6 | Kalbadevi |
| 7 | Girgaon |
| 8 | Grant Road Metro |
| 9 | Mumbai Central Metro |
| 10 | Mahalaxmi Metro |
| 11 | Science Museum |
| 12 | Acharya Atre Chowk |
| 13 | Worli |
| 14 | Siddhivinayak |
| 15 | Dadar Metro |
| 16 | Shitladevi Temple |
| 17 | Dharavi |
| 18 | Bandra Metro |
| 19 | Vidyanagri |
| 20 | Santacruz |
| 21 | CSIA (Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport (Domestic) |
| 22 | Sahar Road |
| 23 | CSIA (Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport (International) |
| 24 | Marol Naka |
| 25 | MIDC |
| 26 | SEEPZ |
| 27 | Aarey Depot Station (Within depot premises) |
In Mumbai, the financial capital of India, the existing suburban rail system was under extreme pressure; more than 11 million people travel by public transport daily. Due to the practical constraints in expanding the existing road and rail networks many pockets in the suburbs and the Island city could not be connected by rail based transport system. With the aim of improving traffic and transportation scenario in Mumbai Metropolitan Region (MMR), the Mumbai Metropolitan Region Development Authority in conjunction with Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) prepared the Master Plan for Mumbai Metro. Priority was given to the areas that were not connected by existing Suburban Rail System. Metro would provide interchange facilities for connecting neighbouring areas like Thane, Navi Mumbai, Vasai, Virar etc.
The long wait of the commuters of Mumbai for the much-needed relief came to an end with the launch of metro line in the city. The Mumbai metro service was launched in the city on 8 June 2014, around 10:10 in the morning. It was flagged off by the Chief Minister of Maharashtra Prithviraj Chavan at the Versova station. The chief minister took a ride from Versova to Ghatkopar (Line 1) in the metro. Also, the ADAG Chairman Anil Ambani and his wife Tina Ambani were present at the inauguration. The line became functional for the common public at 1 p.m.
With the beginning of the metro line in the city, Mumbai has entered the list of cities having metro rail service in the country. The cities already existing in the list are Kolkata, Delhi and Bangalore.
The Mumbaikars have begun to enjoy the convenience of the metro train. However, as far as the fares go, the public will feel the pinch on account of a recent court ruling. The ruling settles the dispute between the Maharashtra government and Reliance Infrastructure, allowing the latter to implement its own fare structure. This increase is expected as the project cost has jumped a whopping 70% from its initial estimates.
According to the Mumbai Metro officials, the metro service has been started for the public only after thorough trial runs. A welcome innovation in the Mumbai Metro has been the introduction of "influence zones" aimed at reducing congestion during peak hours; under this provision, the area within 100 metres of the metro stations will be banned for hawkers and other encroachment.
Mumbai Metro Line 1 (Versova-Andheri-Ghatkopar) is an 11.40 km elevated corridor providing connectivity between Eastern and Western suburbs to Central Railway. It facilitates a smooth interchange - at Andheri and Ghatkopar Stations - between suburban rail system and MRT System thus reducing current travel time by more than 40 minutes.
Mumbai Metro Line 2A (DAHISAR-D.N.NAGAR) is an 18.589 km. long elevated corridor with 17 stations providing interconnectivity among the existing Western Express Highway, Western Railway, Metro Line 1 (Ghatkopar to Versova), Metro Line 2B (D.N.Nagar to Mandale - ongoing), Metro Line 7 (Andheri (E) to Dahisar (E)) and Metro Line 6 (Swami Samarth Nagar to Vikhroli - proposed). The interchange stations at Dahisar and D.N.Nagar provide inter-connectivity between Western, Central and the Northern suburban Mumbai reducing upto 70% of the current travel time.
Mumbai Metro Line 2B (D.N.NAGAR-MANDALE) is 23.643 km. long elevated corridor and has 22 stations connecting the existing Western Express Highway, Eastern Express Highway, Western Railway, Central Railway, Mono Rail, Metro Line 1 (Ghatkopar to Versova), Metro Line 2A (Dahisar to D.N.Nagar), Metro Line 3 (Colaba to SEEPZ - under implementation) and Metro Line 4 (Wadala to Kasarvadavali). It will also provide connectivity between Eastern and Western Suburban Mumbai reducing the current travel time considerably.
Mumbai Metro Line 4 (WADALA-KASARVADAVALI) is 32.32 km. long elevated corridor with 32 stations to inter-connect the existing Eastern Express Roadway, Central Railway, Mono Rail, Metro Line 2B (D.N.Nagar to Mandale - ongoing), Metro Line 5 (Thane to Kalyan - proposed), Metro Line 6 (Swami Samarth Nagar to Vikhroli - proposed) and Metro Line 8 (Wadala to General Post Office) reducing the current travel time to up to 75%.
Mumbai Metro Line 7 (ANDHERI EAST - DAHISAR EAST) is 16.475 km. long elevated corridor with 13 stations inter-connecting the existing Western Express Highway, Western Railway, Metro Line 1 (Ghatkopar to Versova), Metro Line 2A (Dahisar to D.N.Nagar -ongoing) and Metro Line 6 (Swami Samarth Nagar to Vikhroli - proposed). Interchange facility with the suburban rail system and MRT is at Andheri, JVLR and Dahisar. Apart from connecting Central Mumbai and Northern suburban Mumbai, this corridor would provide rail based access to the Mumbai International Airport (CSIA).
Mumbai Trans Harbour Metro Link (MTHL) corridor has been planned by MMRDA from Prabhadevi to Sewri moving further to the Mainland through Navi Mumbai on the Panvel-Pen section. This link will accelerate development on the mainland and also facilitate decongestion on other transport systems.
Maharashtra government was looking for means to better the traffic and transportation scene in Mumbai. The government wanted to come up with something that would meet the future travel needs of the commuters well. It was this exploration of idea that brought various options of mass transit system in the picture. A detailed study was done in this area under the guidance of Indo-German Technical Co-operation by assigning the consultancy work to TEWET in alliance with DE-Consult and TCS in the year 1997-2000. A mass transit passage from Andheri to Ghatkopar was recommended in the study. Meanwhile, DMRC (Delhi Metro Rail Corporation) chalked out the master plan for Mumbai metro, suggesting an extension of Andheri-Ghatkopar route to Versova. Subsequently, the construction work of the metro system in Mumbai gained pace and was performed under the Public Private Partnership (PPP) format.